As structured financial products take center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Structured financial products play a vital role in modern markets, offering a unique blend of complexity and opportunity for investors. Let’s delve into the intricate world of structured financial products and unravel their significance in today’s financial landscape.
Overview of Structured Financial Products
Structured financial products are specialized investments created to meet specific needs that traditional financial products may not address. These products are designed to provide tailored solutions to investors seeking a combination of risk and return that suits their preferences.
Types of Structured Financial Products
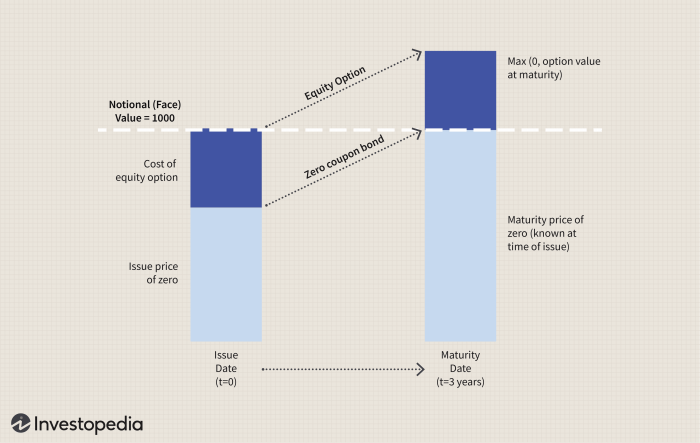
- Structured Notes: These are debt securities with returns linked to the performance of an underlying asset, index, or benchmark. They offer customization and flexibility in terms of risk and return profiles.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits offered by banks with a fixed interest rate and maturity date. Structured CDs may offer variable returns based on market conditions or other factors.
- Structured Warrants: Warrants give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price within a certain period. Structured warrants have additional features like leverage or protection mechanisms.
Design and Structure of Structured Financial Products
In the world of structured financial products, the design and structure play a crucial role in determining the success and effectiveness of these complex investment instruments. Let’s dive into the process of designing structured financial products and the key elements involved in their structuring.
Process of Designing Structured Financial Products
When designing structured financial products, financial institutions and investment firms work closely with experts in quantitative analysis, risk management, and product development. The process typically involves:
- Identifying the investment goals and objectives of the product
- Conducting market research and analysis to understand the target market
- Developing a pricing model based on the desired risk-return profile
- Structuring the product to meet regulatory requirements and investor preferences
Key Elements in Structuring Financial Products
The key elements involved in structuring financial products include:
- Underlying Assets: These are the assets on which the structured product’s returns are based.
- Payoff Structure: This defines how the returns of the product are determined and paid out to investors.
- Tenor: The length of time until the product matures and investors receive their principal and returns.
- Risk Management Strategies: These are crucial to mitigate risks associated with the product, such as market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk.
Risk management strategies are essential in structuring financial products to ensure that investors are protected from potential losses and the product performs as intended.
Risk Management Strategies in Structuring Financial Products
Risk management strategies used in structuring financial products include:
- Diversification: Spreading the investment across different assets to reduce concentration risk.
- Hedging: Using derivatives or other instruments to offset potential losses from adverse market movements.
- Stress Testing: Simulating extreme market scenarios to assess the impact on the product’s performance.
Benefits and Risks of Structured Financial Products
Investing in structured financial products can offer several benefits to investors. These products are designed to provide exposure to a wide range of assets and markets, allowing investors to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional options. Additionally, structured products often come with built-in risk management features, such as downside protection or guaranteed returns, which can help investors minimize losses in volatile markets.
Benefits of Structured Financial Products
- Enhanced Diversification: Structured products offer exposure to different asset classes, sectors, and geographies, helping investors spread their risk.
- Risk Management: Many structured products come with risk mitigation features like capital protection or stop-loss mechanisms to safeguard investments.
- Potential for Higher Returns: Some structured products are designed to provide enhanced returns compared to traditional investments, depending on market conditions.
- Customization: Investors can choose structured products tailored to their risk tolerance, investment goals, and market outlook, providing a personalized investment solution.
Risks of Structured Financial Products
- Complexity: Structured products can be complex and difficult to understand, leading to potential confusion or misinterpretation of the investment terms and conditions.
- Lack of Liquidity: Certain structured products may have limited liquidity, making it challenging for investors to sell their positions before maturity, especially in volatile markets.
- Counterparty Risk: Investors face the risk of default by the issuer or counterparty of the structured product, which can result in total or partial loss of the investment.
- Market Risk: Structured products are exposed to market fluctuations, and investors may not fully benefit from positive market movements if the underlying assets underperform.
Comparison with Traditional Investment Options
- Diversification: While traditional investments like stocks and bonds offer diversification benefits, structured products can provide exposure to unique asset classes and strategies.
- Risk Management: Structured products often incorporate risk mitigation features not found in traditional investments, offering additional protection against market downturns.
- Customization: Structured products allow for greater customization based on investor preferences, providing tailored solutions beyond the standard offerings of traditional investments.
- Return Potential: Depending on market conditions and the structure of the product, structured investments may offer higher returns compared to traditional options, albeit with added complexity and risk.
Market Trends and Regulations
In the world of structured financial products, keeping an eye on market trends and regulations is crucial. Let’s dive into the current landscape and the rules that govern these products.
Current Market Trends
- Increased demand for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) structured products due to growing focus on sustainability.
- Rise of digital structured products leveraging technology like blockchain for enhanced security and efficiency.
- Shift towards customized structured products to meet specific investor needs and risk profiles.
Regulatory Framework
- The regulatory framework for structured financial products is overseen by entities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S. and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK.
- Regulations aim to protect investors by ensuring transparency, disclosure of risks, and compliance with market standards.
- Changes in regulations can impact the issuance and trading of structured products, influencing product design, pricing, and market accessibility.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
- Stricter regulations may lead to higher compliance costs for issuers, affecting the availability and pricing of structured products.
- Changes in disclosure requirements can impact investor confidence and the overall market liquidity of these products.
- Regulatory updates can also drive innovation in product structures to align with new compliance standards and market expectations.






