Ready to dive into the world of investment portfolios? Buckle up as we take you through the ins and outs of creating a solid investment strategy that’s as cool as your favorite high school playlist.
From understanding the concept to selecting investments and monitoring your portfolio, we’ve got you covered every step of the way.
Understanding Investment Portfolio
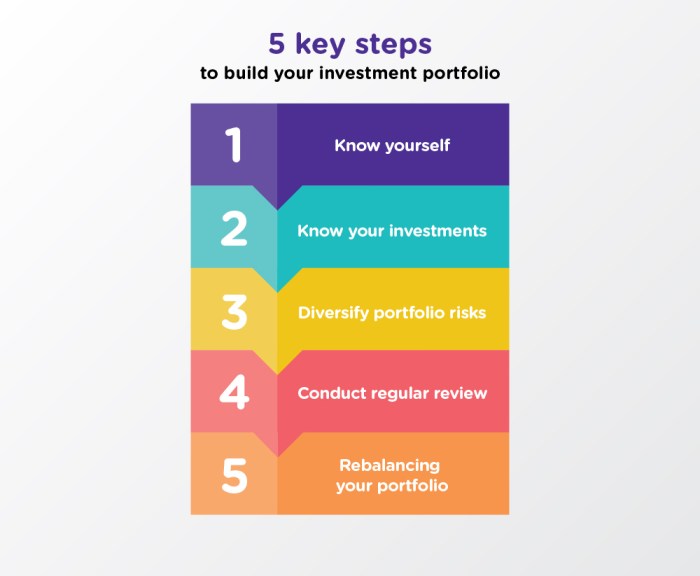
Investment portfolio refers to a collection of financial assets owned by an individual or institution. These assets can include stocks, bonds, real estate, mutual funds, and other investment vehicles.
Diversification is a key concept in building a portfolio as it helps spread risk across different assets. By investing in a variety of asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of volatility in any one investment on the overall portfolio.
Importance of Diversification
Diversification is crucial in building an investment portfolio as it helps mitigate risk. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions, investors can minimize the impact of a single event on their overall portfolio.
- Different Asset Classes: Stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash are examples of asset classes that can be part of a diversified portfolio.
- Risk Tolerance: This refers to an individual’s ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. Understanding your risk tolerance is essential in determining the right mix of assets for your portfolio.
Setting Investment Goals
Setting investment goals is crucial to building a successful investment portfolio. By defining your objectives, you can create a roadmap to guide your investment decisions and monitor your progress over time.
Short-term Investment Goals:
Short-term investment goals typically span one to three years and focus on achieving specific outcomes in the near future. Examples of short-term financial objectives include saving for a vacation, purchasing a new car, or building an emergency fund. These goals are usually less risky and require more liquidity to access funds quickly when needed.
Long-term Investment Goals:
Long-term investment goals extend beyond three years and involve planning for major life events such as retirement, buying a home, or funding a child’s education. These objectives require a more strategic approach, often involving a diversified portfolio with a mix of assets to maximize returns over an extended period. Long-term goals may also involve higher risk tolerance to achieve higher returns.
Aligning Investments with Specific Goals:
It’s essential to align your investments with your specific goals to ensure that your portfolio is tailored to meet your financial needs. For example, if your goal is to save for retirement, you may choose to invest in long-term growth assets like stocks and real estate. On the other hand, if you’re saving for a short-term goal like a down payment on a house, you may opt for more conservative investments like bonds or high-yield savings accounts.
Ultimately, setting clear investment goals helps you stay focused, disciplined, and motivated to build a portfolio that aligns with your financial aspirations.
Assessing Risk Tolerance
When it comes to building an investment portfolio, assessing your risk tolerance is crucial. Understanding how much risk you are willing to take on can help determine the right mix of investments for your portfolio.
To determine your individual risk tolerance, consider factors such as your age, financial goals, investment experience, and comfort level with market fluctuations. Younger investors with a longer time horizon may be more willing to take on higher levels of risk, while older investors nearing retirement may prefer a more conservative approach.
Impact of Risk Tolerance on Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the process of dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. Your risk tolerance plays a significant role in determining the allocation of these assets.
Investors with a higher risk tolerance may choose to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to stocks, which historically offer higher returns but also come with increased volatility. On the other hand, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a larger allocation to bonds or cash equivalents, which are generally considered less risky but offer lower potential returns.
Strategies for Balancing Risk and Return
To strike a balance between risk and return in your portfolio, consider the following strategies:
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce the impact of a downturn in any one sector.
- Rebalancing: Regularly review and adjust your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation mix based on your risk tolerance.
- Asset Allocation: Determine the right mix of stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Risk Management: Use tools like stop-loss orders or options to mitigate potential losses in your portfolio.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation is the process of spreading investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to achieve a balance between risk and return in a portfolio. It plays a crucial role in portfolio management as it helps investors diversify their investments and manage risk effectively.
Types of Asset Allocation Models
- Strategic Asset Allocation: This model involves setting a target mix of asset classes and rebalancing the portfolio back to this target periodically. It is a long-term approach based on the investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: This model involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions and economic outlook. It aims to take advantage of short-term opportunities while still adhering to the overall strategic allocation.
- Dynamic Asset Allocation: This model involves actively changing the asset mix in response to changing market conditions. It requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of the portfolio to capitalize on market trends.
Role of Rebalancing in Asset Allocation
Rebalancing is the process of realigning a portfolio back to its target asset allocation by buying or selling assets. It helps maintain the desired risk and return characteristics of the portfolio over time. By rebalancing, investors can ensure that their portfolio stays in line with their investment objectives and risk tolerance levels.
Selecting Investments
Investing in suitable securities is crucial for building a diversified and profitable investment portfolio. Researching and selecting the right investments can help investors achieve their financial goals and manage risk effectively.
Criteria for Evaluating Investments
When evaluating individual securities or funds for inclusion in a portfolio, investors should consider various criteria such as:
- Historical performance: Analyze the past performance of the investment to assess its potential for future growth.
- Risk factors: Evaluate the risk associated with the investment, including volatility and potential losses.
- Expense ratios: Consider the fees and expenses associated with the investment, as high costs can eat into returns.
- Management team: Assess the expertise and track record of the fund managers or company executives managing the investment.
- Market trends: Analyze current market trends and economic conditions to determine the suitability of the investment.
Examples of Investment Options
Investors have a wide range of investment options across various asset classes to choose from. Some examples include:
- Stocks: Investing in shares of publicly traded companies, offering potential for capital appreciation and dividends.
- Bonds: Purchasing fixed-income securities issued by governments or corporations, providing regular interest payments and return of principal.
- Real Estate: Investing in properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs) for rental income and potential property value appreciation.
- Commodities: Trading in physical goods such as gold, oil, or agricultural products to diversify a portfolio and hedge against inflation.
Monitoring and Rebalancing
Regularly monitoring an investment portfolio is crucial to ensure that it aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By keeping a close eye on your investments, you can make informed decisions and take necessary actions to maintain a balanced portfolio.
Importance of Monitoring
- Monitoring allows you to track the performance of your investments and make adjustments as needed.
- It helps you stay informed about market trends and economic conditions that may impact your portfolio.
- Regular monitoring can help you identify when it’s time to rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation.
Indicators for Rebalancing
- Significant market fluctuations that cause your asset allocation to deviate from your target percentages.
- Changes in your financial goals or risk tolerance that require a shift in your investment strategy.
- New investment opportunities that may better align with your objectives and require portfolio adjustments.
Adjusting Asset Allocation Process
- Review your current asset allocation and compare it to your target allocation.
- Identify which asset classes are over- or under-weighted based on your targets.
- Sell or buy assets to realign your portfolio with your desired allocation.
- Consider the tax implications of rebalancing and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Tax Considerations
When building an investment portfolio, it’s crucial to consider the impact of taxes on your returns. Taxes can eat into your profits, so implementing tax-efficient strategies is key to maximizing your investment gains. Let’s dive into some important tax considerations to keep in mind.
Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
- Utilize tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s to benefit from tax-deferred or tax-free growth.
- Consider holding investments for the long term to qualify for lower capital gains tax rates.
- Opt for tax-efficient investment vehicles like index funds or ETFs that have lower turnover ratios, reducing taxable events.
Impact of Taxes on Investment Returns
- Taxes can significantly reduce your investment returns, especially if you’re in a high tax bracket.
- Capital gains taxes can eat into your profits when selling investments, affecting your overall portfolio performance.
- Understanding the tax implications of different investment types can help you make informed decisions to minimize tax burdens.
Tips for Minimizing Tax Liabilities
- Harvest tax losses strategically to offset gains and reduce your taxable income.
- Consider tax-efficient asset allocation by placing tax-inefficient investments in tax-advantaged accounts.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to optimize tax efficiency and minimize unnecessary tax liabilities.






