Diving into the realm of fixed-income investments, this sets the stage for an intriguing exploration of this financial topic that will leave you wanting more.
What are Fixed-Income Investments?
Fixed-income investments are financial assets that provide investors with a fixed periodic return on their investment. This fixed income is typically in the form of interest payments, dividends, or other regular payments. Unlike stocks, which represent ownership in a company and have variable returns, fixed-income investments offer a predictable income stream.
Types of Fixed-Income Investments
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations. Investors lend money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits offered by banks and credit unions that pay a fixed interest rate over a specified term. They are considered low-risk investments.
- Treasury Securities: These are debt securities issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury, including Treasury bills, notes, and bonds. They are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
- Preferred Stocks: Preferred stocks are hybrid securities that have characteristics of both stocks and bonds. They typically pay a fixed dividend and have priority over common stocks in receiving dividends and assets in case of liquidation.
Characteristics of Fixed-Income Investments
- Fixed Returns: Fixed-income investments offer a predictable stream of income, making them suitable for investors seeking stable cash flow.
- Low Risk: Compared to stocks, fixed-income investments are generally considered to be lower risk due to their fixed returns and priority in receiving payments.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: The value of fixed-income investments may fluctuate based on changes in interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, and vice versa.
- Maturity Dates: Fixed-income investments have specific maturity dates, at which the principal amount is repaid to the investor. This allows investors to plan for future cash flows.
Benefits of Fixed-Income Investments
Investing in fixed-income securities comes with a range of benefits that make them attractive to investors looking for stability and income.
Steady Income Stream
Fixed-income investments, such as bonds, provide investors with a predictable and steady income stream in the form of interest payments. This can be especially beneficial for retirees or those looking for regular cash flow.
Risk-Return Profile
Compared to other asset classes, fixed-income investments generally have a lower risk profile while still offering competitive returns. This balance between risk and return can help investors achieve their financial goals without exposing themselves to excessive volatility.
Diversification
Including fixed-income investments in a portfolio can help diversify risk and reduce overall portfolio volatility. When stocks or other investments are experiencing volatility, fixed-income securities can provide stability and act as a buffer against market fluctuations.
Types of Fixed-Income Investments
Fixed-income investments come in various forms, each with its own characteristics and risk profiles. Understanding the different types can help investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their funds.
Bonds
Bonds are one of the most common types of fixed-income securities. When an investor purchases a bond, they are essentially lending money to the issuer (whether it’s a government entity or a corporation) in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of the initial investment at the bond’s maturity date.
Treasury Bills
Treasury bills, also known as T-bills, are short-term government securities that mature in less than a year. They are considered one of the safest fixed-income investments since they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
Certificates of Deposit
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are time deposits offered by banks and credit unions. Investors deposit a fixed amount of money for a specified period, and in return, they receive interest payments until the CD reaches maturity.
Government vs. Corporate Bonds
Government bonds are issued by federal, state, or local governments to finance public projects and operations. They are generally considered safer than corporate bonds since they are backed by the government’s ability to tax and print money. In contrast, corporate bonds are issued by companies to raise capital, and their creditworthiness is based on the financial health of the issuing company.
Credit Ratings
Credit ratings play a crucial role in fixed-income investments as they provide an assessment of the issuer’s ability to repay its debt. Ratings agencies like Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s, and Fitch assign grades based on the issuer’s creditworthiness, helping investors gauge the risk associated with a particular investment.
Inflation Impact
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-income investments over time. When inflation rises, the interest payments received from fixed-income securities may not keep pace with the increasing cost of goods and services, resulting in a decrease in real returns for investors. To combat inflation risk, investors may consider investing in inflation-protected securities like Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS).
Considerations for Investing in Fixed-Income Securities
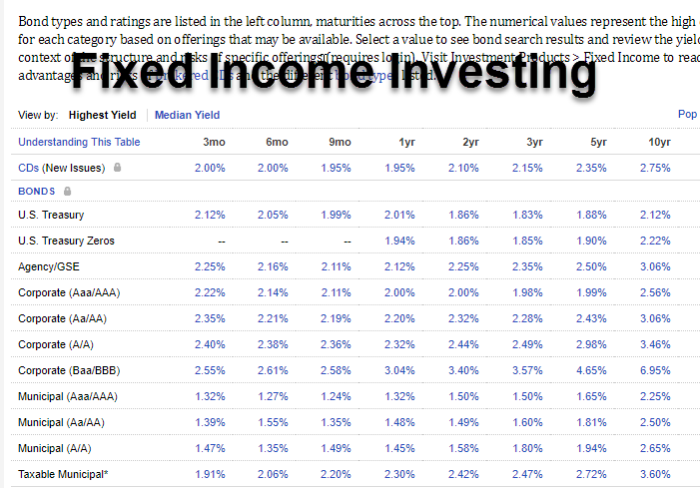
When it comes to investing in fixed-income securities, there are several factors to consider in order to make informed decisions. Understanding how interest rates impact these investments, managing interest rate risk, and building a diversified portfolio are key considerations for investors.
Factors to Consider when Choosing Fixed-Income Investments
- Duration of Investment: Determine the length of time you plan to hold the investment.
- Yield: Evaluate the potential return on investment based on the interest rate offered.
- Risk Tolerance: Consider your risk tolerance and choose investments that align with your financial goals.
How Interest Rates Impact Fixed-Income Securities
Interest rates have a significant impact on the value of fixed-income securities. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds decreases, while falling interest rates increase bond values. This inverse relationship is important to consider when investing in fixed-income securities.
Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk in Fixed-Income Investments
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different types of fixed-income securities to reduce risk.
- Ladder Strategy: Invest in bonds with staggered maturity dates to minimize the impact of interest rate changes.
- Interest Rate Hedging: Consider using interest rate derivatives to hedge against interest rate risk.
Tips for Building a Diversified Fixed-Income Portfolio
- Asset Allocation: Allocate your investments across various fixed-income securities to spread risk.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on potential investments to ensure they align with your financial objectives.
- Rebalancing: Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain diversification and adjust to market changes.






