Diving into the world of dollar-cost averaging, this guide is all about making your money work smarter, not harder. Get ready to learn the ins and outs of this investment strategy that’s got everyone talking.
Whether you’re a newbie investor or a seasoned pro, understanding how to navigate the ups and downs of the market with dollar-cost averaging can be a game-changer for your financial goals. So, buckle up and let’s explore this money move together.
What is Dollar-Cost Averaging?
Dollar-cost averaging is an investment strategy where an investor regularly purchases a fixed dollar amount of a particular investment, regardless of the share price. This approach helps to mitigate the impact of market volatility by spreading out the cost of purchasing shares over time.
How Dollar-Cost Averaging Works
Let’s say you decide to invest $100 in a particular stock every month. If the stock price is high, you will be able to purchase fewer shares with your $100. Conversely, if the stock price is low, you will be able to purchase more shares with the same amount of money. Over time, this strategy can help reduce the impact of market fluctuations on your overall investment.
Benefits of Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Minimizes the risk of making poor investment decisions based on market timing.
- Helps in diversifying the average cost of entry into an investment.
- Can lead to a lower average cost per share over time.
- Provides a disciplined approach to investing regularly.
How to Implement Dollar-Cost Averaging?
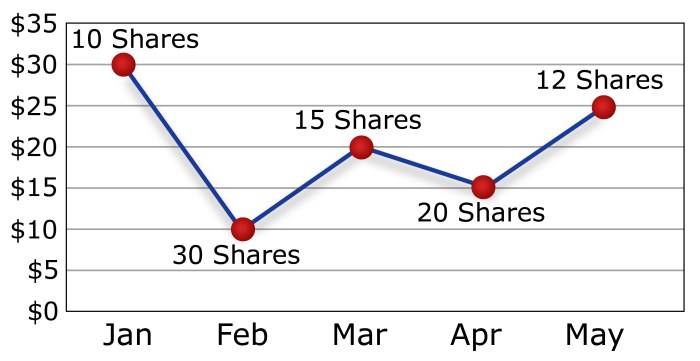
Implementing dollar-cost averaging is a straightforward strategy that can help investors mitigate risks and benefit from market fluctuations over time. By following a few simple steps, you can start building your investment portfolio using this method.
Starting Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Open a brokerage account: To begin dollar-cost averaging, you’ll need to open a brokerage account with a reputable financial institution.
- Choose your investment: Select the investment vehicle you want to use for dollar-cost averaging, such as mutual funds, ETFs, or individual stocks.
- Set up automatic contributions: Schedule regular automatic contributions to your chosen investment at consistent intervals, such as monthly or quarterly.
Choosing the Right Investment Vehicles
- Consider diversification: Opt for investments that provide diversification to spread risk across different asset classes.
- Research fees and expenses: Look for investments with low fees and expenses to maximize your returns over time.
- Assess historical performance: Review the historical performance of the investment vehicle to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Frequency and Amount Considerations
- Frequency: Determine how often you want to make contributions based on your financial situation and investment goals. Regular contributions can help smooth out market volatility.
- Amount: Decide on the amount you want to invest with each contribution. You can start with a small amount and increase it over time as your financial situation improves.
- Stay disciplined: Stick to your contribution schedule and avoid trying to time the market. Consistency is key when implementing dollar-cost averaging.
Dollar-Cost Averaging vs. Lump Sum Investing
When it comes to investing, two common strategies are dollar-cost averaging and lump sum investing. Let’s break down the key differences between the two approaches.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This strategy helps reduce the impact of market volatility on your investments.
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
1. Helps mitigate the risk of investing a large sum of money at the wrong time.
2. Encourages disciplined investing habits over time.
3. Smoothes out the highs and lows of market fluctuations.
1. May result in missed opportunities for higher returns during bull markets.
2. Could lead to lower overall returns compared to lump sum investing in a steadily rising market.
3. Requires ongoing commitment to regular investments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lump Sum Investing
- Lump sum investing involves investing a large amount of money in a single transaction. This approach requires a significant upfront investment but has its own set of pros and cons.
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
1. Potential for higher returns, especially in a rapidly growing market.
2. Immediate exposure to market growth potential.
3. Can benefit from compounding returns over a longer period.
1. Higher risk of market timing errors.
2. Subject to the full impact of market volatility.
3. Psychological stress of a large, single investment.
Real-Life Scenarios
- Imagine Sarah, who decides to invest $1,000 every month in a diversified portfolio using dollar-cost averaging. Despite market fluctuations, Sarah stays committed to her investment plan, benefiting from averaging out her purchase prices over time.
- On the other hand, Joe receives a significant inheritance and chooses to invest the entire amount in one go through lump sum investing. If the market experiences a downturn shortly after Joe’s investment, he may face a temporary loss on his investment.
Maximizing Returns with Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a smart investment strategy that involves consistently investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. By doing so, investors can take advantage of market fluctuations and potentially maximize their returns over the long term.
Optimizing Returns
- Stick to a disciplined investment schedule: Consistently investing a fixed amount at regular intervals, such as monthly or quarterly, can help smooth out market volatility and reduce the impact of emotional decision-making on investments.
- Diversify your investments: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and potentially increase returns. This can help offset losses in one area with gains in another.
- Review and adjust your strategy: Regularly monitor your investments and make adjustments as needed based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Market Volatility Impact
- Market volatility can work in your favor: During market downturns, your fixed investment amount can buy more shares at lower prices, potentially increasing your returns when the market recovers.
- Stay focused on the long term: Market fluctuations are a normal part of investing, and by staying invested and sticking to your dollar-cost averaging strategy, you can benefit from long-term wealth accumulation despite short-term market ups and downs.
- Embrace volatility as an opportunity: Instead of fearing market volatility, see it as a chance to buy more shares at discounted prices, ultimately leading to higher returns when the market rebounds.
Long-Term Wealth Accumulation
- Consistency is key: By consistently investing a fixed amount over time, you can benefit from the power of compounding and potentially achieve significant wealth accumulation in the long run.
- Focus on the big picture: Avoid getting caught up in short-term market fluctuations and instead stay focused on your long-term financial goals. Over time, the ups and downs of the market tend to even out, and consistent investing can help you reach your objectives.
- Patience pays off: Building wealth through dollar-cost averaging requires patience and a long-term perspective. By staying committed to your investment strategy, you can maximize your returns and achieve your financial goals over time.






