With risk management in finance at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling american high school hip style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Risk management in finance is like navigating the halls of high school – you gotta know who to trust, where to turn, and how to avoid the pitfalls. It’s all about making smart moves to protect your financial future and secure those A+ returns.
Importance of Risk Management in Finance
Risk management plays a crucial role in the field of finance as it helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that could impact their financial stability and performance. By implementing effective risk management practices, companies can protect themselves from unexpected events and uncertainties, ultimately safeguarding their investments and assets.
Examples of Effective Risk Management Practices
- Diversification: Investing in a variety of assets to spread risk and reduce the impact of market fluctuations.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like options and futures to protect against adverse price movements.
- Stress testing: Simulating different scenarios to assess how a portfolio or investment would perform under adverse conditions.
Consequences of Inadequate Risk Management Strategies
- Financial Losses: Without proper risk management, organizations are more vulnerable to significant financial losses due to market volatility or unforeseen events.
- Reputation Damage: Inadequate risk management can lead to negative publicity and reputational damage, impacting the trust of investors and stakeholders.
- Regulatory Issues: Failure to manage risks effectively can result in non-compliance with regulations, leading to legal penalties and fines.
Types of Financial Risks
When it comes to managing finances, understanding the different types of risks is crucial. Let’s dive into the various financial risks that can impact stability.
Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential losses due to changes in market conditions, such as interest rates, exchange rates, or commodity prices. For example, a sudden increase in interest rates can lead to a decrease in the value of bonds, impacting an investor’s portfolio.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of loss from the failure of a borrower to repay a loan or meet their financial obligations. This can lead to financial institutions facing defaults on loans, affecting their profitability and overall stability.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk arises when a company or individual cannot meet their short-term financial obligations. For instance, if a company does not have enough cash on hand to cover its expenses, it may have to sell assets quickly at a loss to raise funds.
Operational Risk
Operational risk involves the potential losses from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or human errors. This can include fraud, cyber attacks, or even natural disasters impacting the operations of a business, leading to financial losses.
Risk Management Strategies
Risk management strategies are crucial in the financial sector to help organizations minimize exposure to various risks. Common strategies include diversification, hedging, and insurance. These strategies are tailored to specific financial goals and circumstances to ensure effective risk mitigation.
Diversification
Diversification involves spreading investments across different assets to reduce the impact of a single investment’s performance on the overall portfolio. This strategy helps in minimizing the risk associated with a specific asset or sector. By diversifying the portfolio, organizations can lower the overall risk exposure and enhance the potential for returns.
Hedging
Hedging is a strategy that involves taking offsetting positions to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. Organizations use hedging techniques such as options, futures, and swaps to protect against potential losses. Hedging helps in managing risks related to fluctuations in interest rates, currencies, or commodity prices.
Insurance
Insurance is another risk management strategy where organizations transfer the risk of potential losses to an insurance company in exchange for a premium. By purchasing insurance policies for specific risks, organizations can protect themselves against unforeseen events such as natural disasters, accidents, or liability claims.
Overall, these risk management strategies play a crucial role in helping organizations navigate the complex financial landscape by minimizing exposure to various risks. It is essential for organizations to tailor these strategies according to their specific financial goals and circumstances to effectively manage risks and ensure long-term sustainability.
Risk Assessment Techniques: Risk Management In Finance
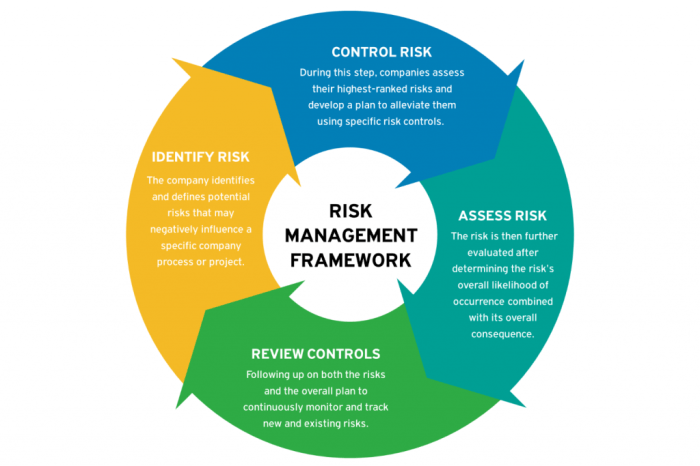
Risk assessment techniques are crucial in evaluating and managing financial risks. These techniques help organizations identify, analyze, and prioritize potential risks to make informed decisions. In finance, both quantitative and qualitative methods are utilized to assess risks effectively.
Quantitative Methods, Risk management in finance
Quantitative methods involve using numerical data and mathematical models to evaluate financial risks. Some common tools and models employed in risk assessment processes include:
- Value at Risk (VaR): A statistical technique used to estimate the maximum potential loss in value of a portfolio over a specific time period under normal market conditions.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: A simulation technique that generates thousands of possible outcomes to assess the impact of different variables on investment portfolios.
- Regression Analysis: A statistical method used to analyze the relationship between different variables and identify potential risks.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods, on the other hand, involve subjective assessments based on expert judgment and historical data. These methods focus on understanding the nature and impact of risks rather than assigning numerical values. Some examples of qualitative risk assessment techniques include:
- SWOT Analysis: A framework used to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with a particular investment or project.
- Scenario Analysis: A method that involves assessing the potential impact of various scenarios on financial outcomes to prepare for unexpected events.
- Expert Interviews: In-depth conversations with industry experts to gather insights and opinions on potential risks and their implications.
Role of Historical Data, Probability Analysis, and Scenario Planning
Historical data, probability analysis, and scenario planning play crucial roles in evaluating potential risks. Historical data provides valuable insights into past trends and patterns, helping organizations anticipate future risks. Probability analysis helps quantify the likelihood of different risk scenarios occurring, enabling better decision-making. Scenario planning involves creating hypothetical situations to assess the impact of various risks on financial outcomes, providing a comprehensive view of potential vulnerabilities.
Regulatory Framework for Risk Management
In the realm of finance, regulatory bodies play a crucial role in setting guidelines and requirements for risk management practices within financial institutions. These regulations are put in place to safeguard the stability of the financial system and protect the interests of investors and the general public.
Regulatory Requirements for Financial Institutions
- Financial institutions are required to establish comprehensive risk management frameworks that identify, assess, and mitigate various types of risks.
- Regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Federal Reserve impose capital adequacy requirements to ensure that financial institutions have enough capital to cover potential losses.
- Financial institutions are mandated to conduct stress tests to evaluate their resilience to adverse market conditions and economic shocks.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
- Regulatory bodies oversee the implementation of risk management practices and ensure that financial institutions comply with regulatory requirements.
- They provide guidance and updates on regulatory changes to help financial institutions adapt their risk management strategies accordingly.
- Regulatory bodies conduct examinations and audits to assess the effectiveness of risk management practices and identify areas for improvement.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
- Regulatory changes can significantly impact risk management practices within the financial industry by requiring institutions to adjust their strategies and policies.
- Changes in regulations may lead to increased compliance costs for financial institutions as they strive to meet the new requirements set by regulatory bodies.
- Regulatory changes can also influence the overall risk culture within financial institutions, prompting them to prioritize risk management and enhance transparency in their operations.
Emerging Trends in Risk Management
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, new trends in risk management are emerging to address the complex challenges faced by financial institutions. These trends focus on leveraging technology and data analytics to enhance risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
Influence of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing risk management processes by enabling real-time analysis of vast amounts of data to identify potential risks and opportunities. These technologies can detect patterns and anomalies that may not be apparent to human analysts, helping financial firms make more informed decisions.
“AI and machine learning algorithms can help financial institutions predict market trends and assess risks more accurately than traditional methods.”
Innovative Risk Management Practices in Financial Firms
- Utilizing predictive analytics to forecast market trends and identify potential risks.
- Implementing automated risk monitoring systems to detect anomalies and mitigate risks in real-time.
- Leveraging blockchain technology for secure and transparent risk management processes.
- Enhancing cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial data from cyber threats.