Diving into the world of loan repayment schedules, we unravel the complexities and intricacies that borrowers often encounter. From understanding the basics to navigating through different types, this guide promises to equip you with the knowledge needed to manage your repayments effectively.
Get ready to explore the components, calculations, and importance of timely payments in the realm of loan repayment schedules.
Overview of Loan Repayment Schedules
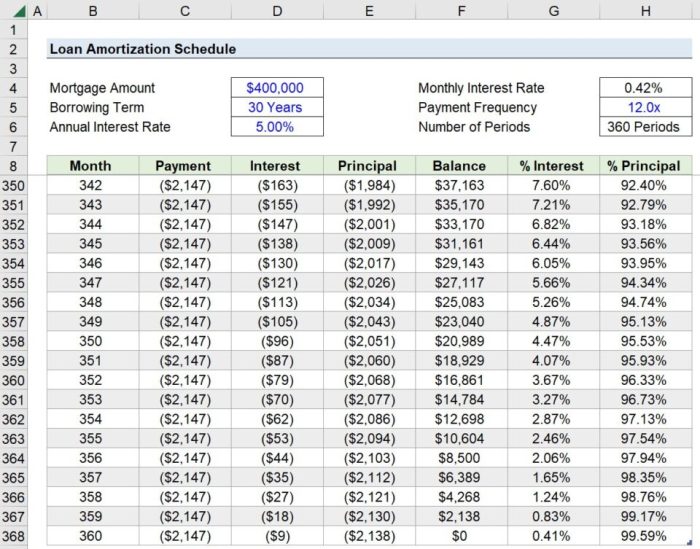
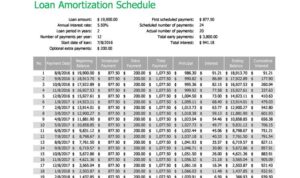
When you take out a loan, a loan repayment schedule Artikels the specific dates and amounts you need to pay back to the lender. It breaks down the principal amount, interest rate, and repayment period into manageable installments.
Types of Loan Repayment Schedules
- Fixed Payment Schedule: In this type, the borrower pays a fixed amount at regular intervals until the loan is fully repaid. This schedule is easier to budget for as the payments remain constant.
- Graduated Payment Schedule: Payments start low and gradually increase over time. This schedule is beneficial for borrowers who expect their income to increase in the future.
- Balloon Payment Schedule: A large final payment is made at the end of the loan term. This schedule is suitable for borrowers who can afford smaller payments initially but have the means to pay off a lump sum later.
Importance of Understanding Loan Repayment Schedules
It is crucial for borrowers to comprehend loan repayment schedules to avoid financial pitfalls. Understanding the schedule helps in planning finances, managing cash flow, and ensuring timely payments to avoid penalties or default.
Components of a Loan Repayment Schedule
When looking at a loan repayment schedule, there are several key components that you need to consider in order to understand how your payments are structured.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
- Fixed Interest Rate: This type of interest rate stays the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will remain constant, providing predictability and stability in your repayment schedule.
- Variable Interest Rate: With a variable interest rate, the interest rate can fluctuate based on market conditions. This can lead to changes in your monthly payments, which may make it harder to budget and plan for your loan repayment.
Impact of Loan Amount, Interest Rate, and Term
- Loan Amount: The total amount of money you borrow will directly impact your monthly payments. The higher the loan amount, the higher your monthly payments will be.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate on your loan will also play a significant role in determining your monthly payments. A higher interest rate means higher monthly payments, while a lower interest rate means lower monthly payments.
- Term: The term of your loan, or the length of time you have to repay it, will also affect your repayment schedule. A shorter term will result in higher monthly payments, but you will pay less in total interest over the life of the loan. On the other hand, a longer term will result in lower monthly payments, but you will end up paying more in total interest.
Calculating Loan Repayment Schedules
When it comes to calculating loan repayment schedules, there are specific mathematical formulas that lenders use to determine the monthly payments. These calculations are crucial for borrowers to understand the overall cost of borrowing and how long it will take to repay the loan.
Mathematical Formulas for Loan Repayment
To calculate monthly payments for a loan, lenders typically use the following formula:
Monthly Payment = [P * r * (1 + r)^n] / [(1 + r)^n – 1]
Where:
– P = Principal loan amount
– r = Monthly interest rate (annual interest rate divided by 12)
– n = Total number of payments (loan term in months)
Step-by-Step Calculation of Monthly Payments
1. Determine the principal loan amount (P), the annual interest rate, and the loan term in years.
2. Convert the annual interest rate to a monthly interest rate by dividing it by 12.
3. Convert the loan term from years to months.
4. Plug the values into the formula mentioned above to calculate the monthly payment amount.
Impact of Different Repayment Frequencies
The frequency of loan repayments, whether monthly, bi-weekly, or weekly, can have a significant impact on the overall loan repayment schedule. For example, making bi-weekly payments instead of monthly payments can result in paying off the loan faster and saving on interest costs over time. This is because with more frequent payments, less interest accrues between payments, reducing the total amount paid over the life of the loan.
Importance of Timely Payments
Paying your loans on time is crucial to avoid facing negative consequences that can affect your financial stability and credit score. When you miss or delay payments, you may incur late fees, penalty charges, and even damage your credit history, making it harder to secure loans in the future.
Consequences of Missing or Delaying Loan Payments
- Accumulation of late fees and penalties, increasing your overall debt.
- Negative impact on your credit score, affecting your ability to borrow money in the future.
- Potential legal action from lenders to recover the unpaid amounts.
Tips for Staying on Track with Repayment Schedules
- Create a budget and prioritize loan payments to ensure they are made on time.
- Set up automatic payments or reminders to avoid missing deadlines.
- Consider consolidating or refinancing your loans to make repayments more manageable.
Strategies for Managing Unexpected Financial Challenges
- Build an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses without impacting your loan payments.
- Contact your lender immediately if you anticipate difficulty in making a payment to explore alternative options.
- Seek financial counseling or assistance to develop a plan for managing unexpected financial hardships.