Dive into the world of dividend payout ratios, where numbers tell a story of financial health and investment potential. Discover why these ratios are crucial for investors and how they can impact stock prices.
Explore the calculations behind dividend payout ratios and how they provide insight into a company’s stability and growth prospects.
Definition of Dividend Payout Ratios
Dividend payout ratios are a financial metric used by investors to evaluate the percentage of earnings that a company pays out to its shareholders in the form of dividends. This ratio provides insight into how much of a company’s profits are being distributed to shareholders versus being reinvested back into the business.
Importance of Dividend Payout Ratios
- Dividend payout ratios help investors assess a company’s dividend policy and sustainability of dividend payments over time.
- High dividend payout ratios may indicate that a company is returning a significant portion of its profits to shareholders, potentially leading to lower reinvestment in growth opportunities.
- Conversely, low dividend payout ratios may suggest that a company is retaining more earnings for future growth and expansion.
Calculation of Dividend Payout Ratios
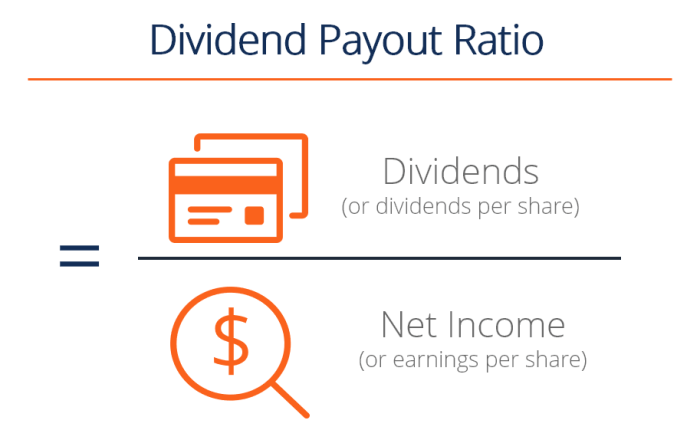
To calculate the dividend payout ratio, you can use the following formula:
Dividend Payout Ratio = Dividends per Share / Earnings per Share
This formula compares the total dividends paid out to shareholders with the earnings generated by the company on a per-share basis. The resulting ratio provides insight into how much of the earnings are being distributed as dividends.
Significance of Dividend Payout Ratios
When it comes to analyzing a company’s financial health and performance, dividend payout ratios play a crucial role. These ratios provide valuable insights into how much of a company’s earnings are being distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends.
Impact of High Dividend Payout Ratios
High dividend payout ratios can indicate that a company is financially stable and generating consistent profits. This can be attractive to investors seeking regular income from their investments. However, excessively high payout ratios may also signal that a company is not reinvesting enough in its operations for future growth.
Relationship between Dividend Payout Ratios and Stock Prices
There is a direct relationship between dividend payout ratios and stock prices. Generally, companies with higher dividend payout ratios tend to have higher stock prices because they are viewed as financially sound and investor-friendly. Investors often favor companies that pay dividends regularly, leading to increased demand for their stocks and potentially driving up their prices.
Reflection of Company’s Financial Health
Dividend payout ratios can serve as an indicator of a company’s financial health. A consistent and sustainable dividend payout ratio over time can signify that a company has a strong balance sheet, stable cash flows, and confidence in its future earnings potential. On the other hand, fluctuating or erratic payout ratios may raise concerns about the company’s financial stability and ability to sustain dividend payments in the long run.
Interpreting Dividend Payout Ratios
When it comes to understanding dividend payout ratios, it’s crucial to look at different scenarios to get a comprehensive view of how they work. Let’s dive into some examples to shed light on the subject.
Examples of Dividend Payout Ratios
- A low dividend payout ratio typically indicates that a company is retaining most of its earnings for reinvestment in the business. For instance, a ratio below 30% might suggest that the company is prioritizing growth over immediate dividends.
- On the other hand, a high dividend payout ratio, say above 70%, could imply that the company is distributing a large portion of its earnings to shareholders. This might be appealing to income-seeking investors but could also signal limited growth opportunities.
- A sustainable dividend payout ratio falls somewhere in the middle, striking a balance between rewarding shareholders and reinvesting in the business for future growth. A ratio between 40-60% is often considered sustainable.
Comparing Dividend Payout Ratios Across Industries
In analyzing dividend payout ratios across different industries, it’s essential to consider the nature of the business, its growth prospects, and capital requirements. For instance, mature industries like utilities or consumer staples tend to have higher payout ratios due to stable cash flows. In contrast, tech or biotech companies might have lower ratios as they reinvest heavily in research and development.
Utilizing Dividend Payout Ratios in Investment Decisions
Investors can leverage dividend payout ratios as a tool to assess a company’s financial health and management’s stance towards rewarding shareholders. A consistent or increasing payout ratio over time could indicate stability and confidence in the business. However, a declining ratio might signal potential financial challenges or a shift in strategy towards retaining earnings for growth.
Factors Influencing Dividend Payout Ratios
When it comes to dividend payout ratios, there are several factors that can influence changes in these ratios. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors and analysts to assess the financial health and stability of a company.
One of the key factors that can impact dividend payout ratios is the company’s profitability. A company that is consistently profitable is more likely to have a higher dividend payout ratio as it has the financial resources to distribute dividends to its shareholders. On the other hand, a company experiencing financial difficulties may have a lower dividend payout ratio or may even suspend dividend payments altogether.
Another factor to consider is the company’s growth prospects. Companies that are in a growth phase may choose to reinvest their profits back into the business rather than distribute them as dividends. This can result in a lower dividend payout ratio as the company prioritizes growth over immediate returns for shareholders.
Additionally, the industry in which a company operates can also influence its dividend payout ratio. Industries that require significant capital investments may have lower dividend payout ratios as they need to retain earnings to fund future growth opportunities. Conversely, companies in more mature industries with stable cash flows may have higher dividend payout ratios.
Impact of Company Growth on Dividend Payout Ratios
Company growth plays a crucial role in determining the dividend payout ratio. As a company grows, it may choose to reinvest its profits into expanding its operations, developing new products, or entering new markets. This can result in a lower dividend payout ratio as the company retains earnings to fuel its growth initiatives. Investors should consider the growth prospects of a company when analyzing its dividend payout ratio as it provides insights into the company’s future financial performance and shareholder returns.
Relationship between Dividend Policies and Dividend Payout Ratios
A company’s dividend policy directly impacts its dividend payout ratio. Companies with a stable dividend policy, where they commit to paying a consistent dividend amount or percentage of earnings, are likely to have a more predictable dividend payout ratio. On the other hand, companies with a flexible dividend policy may adjust their dividend payouts based on various factors such as earnings growth, cash flow availability, and investment opportunities. This flexibility can result in fluctuations in the dividend payout ratio, making it important for investors to understand the company’s dividend policy and its implications on shareholder returns.






