Diving deep into the world of investment risk management, this guide will take you on a journey through the ins and outs of effectively navigating financial risks like a boss. Get ready to level up your investment game with the coolest strategies and techniques in the game.
Introduction to Investment Risk Management
Investment risk management is a crucial component of financial planning that focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with investment strategies. By effectively managing risks, investors can protect their capital, maximize returns, and achieve their financial goals.
Importance of Effective Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential for investors to navigate the unpredictable nature of financial markets and minimize potential losses. It helps in preserving wealth, maintaining a balanced portfolio, and ensuring long-term financial stability.
Key Principles of Managing Investment Risks
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk exposure.
- Asset Allocation: Allocating funds strategically based on risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the risk-return profile of investment opportunities before making decisions.
- Monitoring and Review: Regularly reviewing and adjusting investment strategies to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Contingency Planning: Having contingency plans in place to mitigate unexpected risks and market fluctuations.
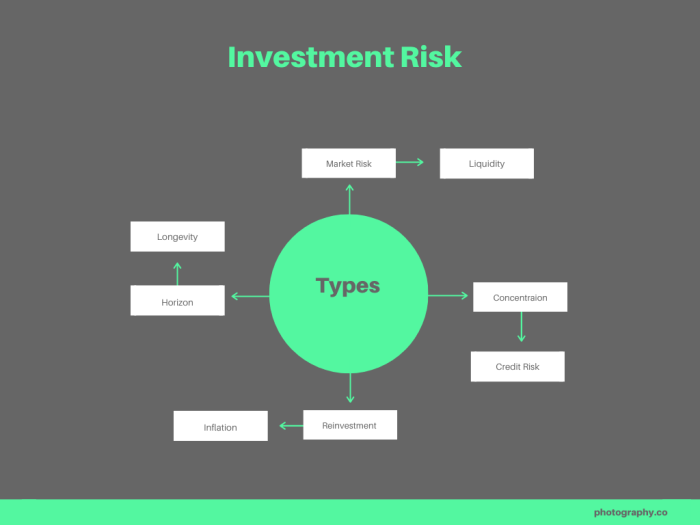
Types of Investment Risks
Investing always comes with risks, and it’s important to understand the different types of risks that can impact your investments. Let’s dive into the various types of investment risks and how they can affect your portfolio.
Market Risk
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to the risk of investments losing value due to factors affecting the overall market. This risk is beyond the control of individual investors and is influenced by economic conditions, political events, and market trends. For example, a sudden economic downturn can lead to a decline in stock prices, impacting the value of your investment portfolio.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of loss resulting from a borrower failing to repay a loan or meet their financial obligations. This type of risk is commonly associated with bonds or other debt securities. For instance, if a company defaults on its bond payments, bondholders may face losses on their investments.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the risk of not being able to sell an investment quickly at a fair price. Investments with low liquidity may have wider bid-ask spreads, making it challenging to execute trades without impacting the market price. For example, if you own shares in a thinly traded stock, you may struggle to sell them quickly without accepting a lower price.
Risk Assessment Techniques
Investment risk management involves various techniques to assess and mitigate risks associated with different types of investments. These techniques help investors make informed decisions and protect their portfolios from potential losses.
Risk Tolerance Assessment
Risk tolerance assessment is a crucial step in understanding an investor’s willingness and ability to take on risk. This assessment helps determine the investor’s comfort level with fluctuations in investment values and their ability to withstand potential losses. By knowing their risk tolerance, investors can align their investment strategies accordingly to achieve their financial goals.
- Investors can assess their risk tolerance through questionnaires provided by financial advisors or online tools.
- Factors such as age, investment goals, financial situation, and investment time horizon are considered in determining risk tolerance.
- Understanding risk tolerance helps investors create a diversified portfolio that matches their risk profile.
Role of Diversification
Diversification plays a crucial role in mitigating investment risks by spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. This strategy helps reduce the impact of a single investment’s performance on the overall portfolio and minimizes the risk of significant losses.
- Diversification can be achieved through investing in different types of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
- By diversifying their portfolio, investors can reduce the correlation between assets and minimize the risk of losing all investments in a single market event.
- Proper diversification can help investors achieve a balance between risk and return, aligning with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Risk Assessment Tools
Risk assessment tools provide investors with quantitative methods to evaluate and manage investment risks effectively. These tools help investors analyze potential risks, identify vulnerabilities in their portfolios, and make informed decisions to protect their investments.
- Common risk assessment tools include Value at Risk (VaR) models, stress testing, Monte Carlo simulations, and scenario analysis.
- Value at Risk (VaR) measures the maximum potential loss an investment portfolio may incur over a specific time period at a certain confidence level.
- Stress testing involves analyzing the impact of extreme market events on a portfolio to assess its resilience under adverse conditions.
- Monte Carlo simulations use random variables to model different investment scenarios and assess the likelihood of achieving specific financial outcomes.
- Scenario analysis helps investors evaluate the impact of various economic, market, or geopolitical events on their portfolios and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Risk Management Strategies
When it comes to managing investment risks, having proactive strategies in place is crucial to safeguard your assets. Two common strategies used by investors are hedging and asset allocation. Hedging involves offsetting potential losses by taking a position in a related security, while asset allocation focuses on diversifying investments across different asset classes to reduce overall risk.
Risk-Return Tradeoff
The concept of risk-return tradeoff is a fundamental principle in investing. It states that higher returns are usually associated with higher levels of risk. This means that investors must carefully consider how much risk they are willing to take on in order to achieve their desired returns. By understanding this tradeoff, investors can make informed decisions about their risk management strategies.
Real-World Examples
In different market conditions, successful risk management strategies have been implemented by various investors. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, many investors who had diversified their portfolios across different asset classes were able to minimize their losses. Similarly, in times of economic uncertainty, some investors use options contracts to hedge against potential market downturns. These real-world examples highlight the importance of having effective risk management strategies in place to navigate volatile market conditions.
Monitoring and Reviewing Risks
In the world of investment risk management, continuous monitoring and reviewing of risks play a crucial role in ensuring the success and sustainability of investment portfolios. By staying vigilant and proactive in assessing risks, investors can make well-informed decisions and take timely actions to mitigate potential threats to their investments.
Key Performance Indicators for Evaluating Risk Management Strategies
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of risk management strategies. These indicators provide valuable insights into the performance of risk management efforts and help investors gauge the success of their risk mitigation plans.
- Sharpe Ratio: A measure of risk-adjusted return, indicating how well an investment has performed relative to its risk level.
- Tracking Error: Measures the divergence of an investment’s performance from its benchmark index, highlighting the effectiveness of portfolio management.
- Value at Risk (VaR): Estimates the maximum potential loss that an investment portfolio may face over a specific time horizon under normal market conditions.
- Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR): Provides a more comprehensive view of potential losses by considering extreme scenarios beyond the VaR threshold.
- Frequency of Risk Events: Tracks the occurrence of risk events and helps investors assess the impact of risks on their portfolios.
Conducting Regular Risk Reviews and Adjustments
Regular risk reviews are essential to ensure that investment portfolios remain aligned with investors’ risk tolerance and objectives. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct effective risk reviews and make necessary adjustments:
- Define Review Periods: Establish a schedule for regular risk reviews based on the complexity and volatility of the investment portfolio.
- Identify Risk Factors: Evaluate the key risk factors affecting the portfolio, including market risks, credit risks, liquidity risks, and operational risks.
- Assess Risk Exposure: Measure the level of risk exposure in the portfolio and compare it against predefined risk limits and thresholds.
- Analyze Risk Mitigation Strategies: Review the effectiveness of existing risk mitigation strategies and identify areas for improvement or adjustment.
- Implement Adjustments: Make necessary adjustments to the investment portfolio based on the findings of the risk review, ensuring alignment with investors’ risk preferences and financial goals.