Venture capital funds set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Get ready to dive into the fascinating realm of venture capital funds and explore the ins and outs of this dynamic investment landscape.
Overview of Venture Capital Funds
Venture capital funds are investment vehicles that provide funding to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. Their primary purpose is to invest in early-stage companies in exchange for equity ownership, with the goal of earning a significant return on investment when the company succeeds.
Unlike other investment vehicles such as mutual funds or hedge funds, venture capital funds focus on investing in companies that are in the early stages of development and have the potential for rapid growth. These funds typically take on higher risks in exchange for the potential of high returns.
Examples of Successful Companies Funded by Venture Capital
Some well-known examples of successful companies that were funded by venture capital include:
- Uber: The ride-sharing company received early funding from venture capital firms like Benchmark and Menlo Ventures, helping it grow into a global transportation giant.
- Facebook: The social media platform received funding from Accel Partners and others in its early stages, leading to its massive success and worldwide reach.
- Google: The search engine giant was initially funded by venture capital firm Sequoia Capital, among others, contributing to its dominance in the tech industry.
Types of Venture Capital Funds
When it comes to venture capital funds, there are different types that cater to various stages of a company’s growth. Let’s explore the characteristics of each type and share examples of prominent funds in each category.
Early-Stage Venture Capital Funds
Early-stage venture capital funds focus on providing funding to startups in the initial stages of development. These funds typically invest in companies with innovative ideas and high growth potential, but may lack a proven business model or revenue. Examples of early-stage venture capital funds include Y Combinator, 500 Startups, and Techstars.
Expansion Venture Capital Funds
Expansion venture capital funds target companies that have already established a product or service in the market and are looking to scale their operations. These funds provide capital for expanding the business, entering new markets, or acquiring other companies. Prominent examples of expansion venture capital funds include Sequoia Capital, Accel Partners, and Andreessen Horowitz.
Late-Stage Venture Capital Funds
Late-stage venture capital funds invest in companies that are nearing an exit, such as an IPO or acquisition. These funds provide capital to help these companies reach the next level of growth before they go public or get acquired. Examples of late-stage venture capital funds include TCV, Insight Partners, and SoftBank Vision Fund.
How Venture Capital Funds Work
Venture capital funds work by providing capital to startup companies in exchange for equity ownership. This process involves raising funds from investors, evaluating potential investments, and supporting the growth of portfolio companies.
Raising Capital from Venture Capital Funds
When venture capital funds are raised, the fund managers typically reach out to institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and other sources of capital. These investors contribute money to the fund, which is then used to invest in startups with high growth potential.
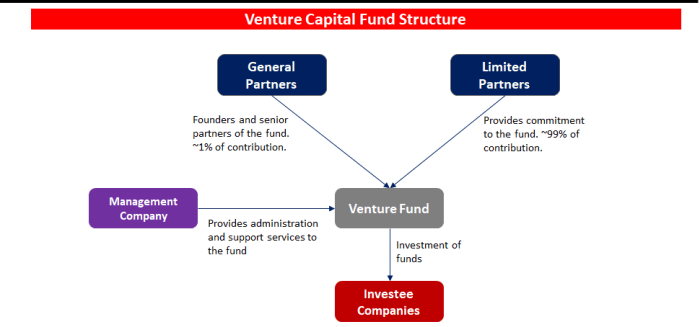
Typical Structure of a Venture Capital Fund
A typical venture capital fund is structured as a limited partnership, with the fund manager serving as the general partner and the investors as limited partners. The fund manager is responsible for making investment decisions and managing the portfolio companies, while the investors provide the capital and share in the profits.
Criteria for Evaluating Potential Investments
Venture capitalists use a variety of criteria to evaluate potential investments, including the strength of the founding team, the size of the market opportunity, the scalability of the business model, and the potential for a high return on investment. They also consider factors such as competitive landscape, product differentiation, and potential exit strategies.
Benefits and Risks of Venture Capital Funding
Venture capital funding can offer numerous benefits to startups, including access to capital, industry expertise, networking opportunities, and guidance from experienced investors. However, there are also risks involved in partnering with venture capital funds, such as loss of control, pressure to meet aggressive growth targets, and potential conflicts with investors over strategic decisions.
Advantages of Securing Funding from Venture Capital Funds
- Access to Capital: Venture capital funds provide startups with the necessary funding to scale their business operations and reach new markets.
- Industry Expertise: Venture capitalists often have extensive experience in specific industries and can offer valuable insights and guidance to help startups navigate challenges.
- Networking Opportunities: By partnering with venture capital funds, startups gain access to a vast network of contacts, including other entrepreneurs, industry leaders, and potential customers.
- Experienced Investors: Venture capitalists bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the table, helping startups make strategic decisions and avoid common pitfalls.
Risks of Partnering with Venture Capital Funds
- Loss of Control: Accepting funding from venture capital funds can result in a loss of control over key business decisions, as investors may have a say in the direction of the company.
- Pressure to Meet Growth Targets: Venture capitalists often expect high returns on their investment and may put pressure on startups to achieve rapid growth, which can lead to unsustainable practices.
- Conflicts Over Strategic Decisions: Differences in vision and priorities between founders and investors can lead to conflicts over strategic decisions, potentially hindering the company’s progress.
Examples of Companies Impacted by Venture Capital Funding
- Success: Airbnb – Securing funding from venture capital funds helped Airbnb expand globally, establish partnerships, and enhance its platform, leading to its current position as a market leader in the hospitality industry.
- Failure: Juicero – Despite raising significant venture capital funding, Juicero failed to gain traction in the market due to high product costs, limited consumer demand, and operational challenges, ultimately leading to its shutdown.
Trends in Venture Capital Funding
Venture capital funding is constantly evolving, adapting to changes in technology and market trends. Understanding the current landscape of venture capital is crucial for entrepreneurs and investors looking to navigate this dynamic industry.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have significantly impacted the venture capital industry, with investors focusing on sectors such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and biotechnology. These emerging technologies present new opportunities for innovative startups to secure funding and disrupt traditional industries.
Emerging Sectors Attracting Venture Capital Investments
- As the world shifts towards sustainability, clean energy startups are attracting a significant amount of venture capital investments. Companies focused on renewable energy sources and eco-friendly solutions are gaining traction in the market.
- The healthcare sector is also experiencing a surge in venture capital funding, particularly in areas such as telemedicine, digital health, and personalized medicine. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital healthcare solutions, making this sector highly attractive to investors.
- E-commerce and direct-to-consumer brands are another hot sector for venture capital investments. With the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behaviors, investors are keen to support startups that are revolutionizing the retail industry.






