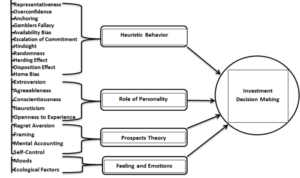
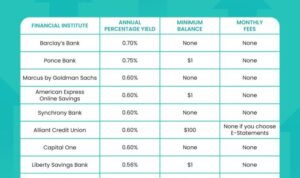
Get ready to dive into the world of Financial goals setting, where we break down the importance of setting financial goals in a way that’s not just informative, but also totally lit. From short-term gains to long-term financial freedom, this introduction sets the stage for a rollercoaster ride of financial empowerment.
As we explore different types of financial goals, strategies for setting them, and ways to monitor and adjust along the way, prepare to level up your financial game in the most swag way possible.
Importance of Financial Goals Setting
Setting financial goals is crucial for personal financial planning because it helps individuals take control of their finances and work towards achieving their desired financial outcomes. Without clear goals, it can be easy to overspend, accumulate debt, or fail to save for the future.
Having clear financial goals provides several benefits, including:
Benefits of Clear Financial Goals
- Increased focus and motivation to save and invest wisely.
- Improved decision-making when it comes to spending and budgeting.
- Ability to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
Financial goals can also provide direction and motivation for financial decisions by:
Providing Direction and Motivation
- Setting a roadmap for short-term and long-term financial success.
- Helping individuals prioritize their spending and saving habits.
- Inspiring individuals to work towards a specific financial milestone or target.
Types of Financial Goals
When setting financial goals, it’s important to consider the timeline in which you want to achieve them. Financial goals can be categorized into three main types: short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals. Each type has its own characteristics and importance in helping you manage your finances effectively.
Short-Term Financial Goals
Short-term financial goals are those that you want to achieve within the next year or so. These goals are usually focused on immediate needs and wants, such as paying off credit card debt, building an emergency fund, or saving for a vacation. Short-term goals are important because they help you stay on track with your finances and provide a sense of accomplishment when achieved.
- Example: Saving $1,000 for an emergency fund within the next 6 months.
- Example: Paying off $2,000 in credit card debt by the end of the year.
Medium-Term Financial Goals
Medium-term financial goals are those that you want to achieve within the next 2-5 years. These goals often involve bigger financial commitments, such as buying a car, saving for a down payment on a house, or starting a business. Medium-term goals are important because they require consistent saving and planning to reach them within the specified timeframe.
- Example: Saving $20,000 for a down payment on a house within the next 3 years.
- Example: Starting a college fund for your child’s education in 5 years.
Long-Term Financial Goals
Long-term financial goals are those that you want to achieve in 5 years or more. These goals are typically focused on retirement planning, building wealth, or leaving a financial legacy for future generations. Long-term goals are important because they require long-term commitment, investment, and planning to ensure financial security in the future.
- Example: Saving $1 million for retirement by the age of 65.
- Example: Investing in a diversified portfolio to build wealth over the next 20 years.
Strategies for Setting Financial Goals

Setting financial goals is an essential step towards achieving financial stability and success. Here are some effective strategies to help you set realistic and achievable financial goals.
SMART Criteria for Setting Financial Goals
- Specific: Clearly define your financial goals in detail. For example, instead of saying “save money,” specify an amount and a timeline.
- Measurable: Make sure your goals can be quantified so that you can track your progress. This could involve setting benchmarks or milestones.
- Achievable: Set goals that are within reach based on your current financial situation, resources, and capabilities. Avoid setting goals that are too lofty or unrealistic.
- Relevant: Your financial goals should align with your overall financial plan and objectives. They should be meaningful and contribute to your long-term financial success.
- Time-bound: Assign a deadline to each financial goal to create a sense of urgency and motivation. This will help you stay focused and committed to achieving them.
Tips on Prioritizing Financial Goals
- Evaluate your financial situation: Take stock of your income, expenses, debts, and savings to understand your current financial standing.
- Identify short-term and long-term goals: Distinguish between goals that need to be achieved in the near future and those that are more long-term.
- Consider your values and priorities: Align your financial goals with what matters most to you, whether it’s saving for a house, retirement, education, or travel.
- Focus on high-priority goals: Prioritize goals that are urgent or critical to your financial well-being. This could include paying off high-interest debts or building an emergency fund.
- Create a timeline: Establish a timeline for each goal based on its importance, urgency, and feasibility. This will help you stay organized and on track.
Monitoring and Adjusting Financial Goals
Setting financial goals is just the first step towards financial success. It is equally important to regularly monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments along the way to ensure you stay on track. Here’s why monitoring and adjusting financial goals are crucial:
Importance of Regularly Monitoring Progress
Regularly monitoring your progress towards your financial goals allows you to stay informed about how well you are doing. It helps you identify any obstacles or challenges that may be hindering your progress and allows you to take corrective actions promptly.
Tracking Financial Goals and Making Adjustments
- Set specific milestones to track your progress – Break down your financial goals into smaller, manageable milestones so you can easily track your progress.
- Use budgeting tools and apps – Utilize budgeting tools and apps to track your income, expenses, and savings to ensure you are sticking to your financial plan.
- Review your goals regularly – Take time to review your financial goals regularly and adjust them as needed based on changes in your circumstances or priorities.
- Seek professional advice – If you’re struggling to meet your financial goals, consider seeking advice from a financial advisor who can provide guidance on how to adjust your goals effectively.
Staying Motivated and Accountable
- Visualize your goals – Create a vision board or visualize the end result of achieving your financial goals to stay motivated and focused.
- Share your goals with someone – By sharing your financial goals with a trusted friend or family member, you can hold yourself accountable and receive support along the way.
- Reward yourself – Celebrate small victories along the way to keep yourself motivated and reinforce positive financial habits.